The Evolution and Importance of Modern Surgical Instruments
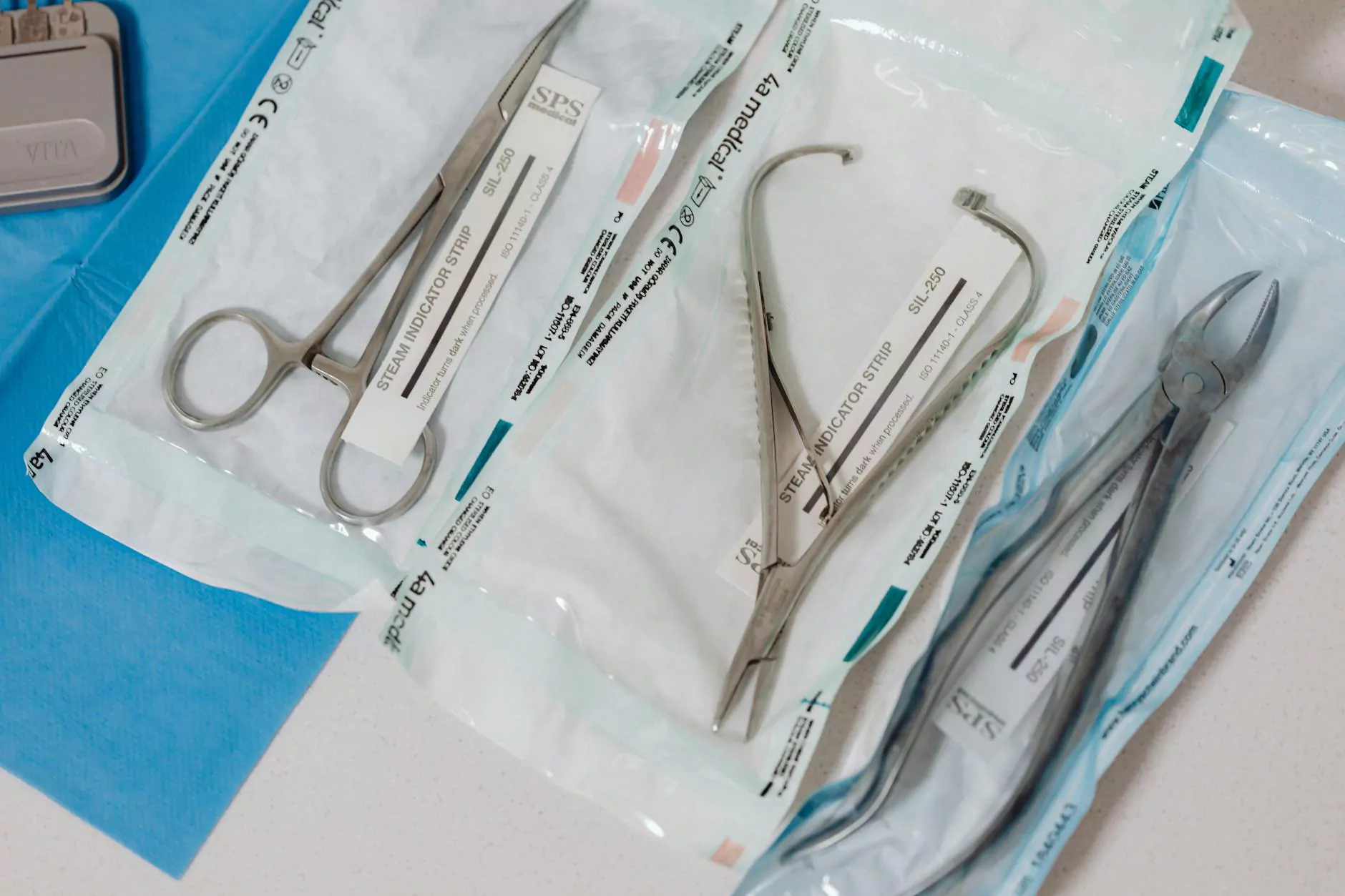
In the realm of healthcare and medical innovations, the development of modern surgical instruments has played a pivotal role in enhancing the quality of surgical procedures, improving patient outcomes, and streamlining the healing process. These instruments are not just tools; they embody decades of research, development, and an unswerving commitment to patient care.
The Historical Context of Surgical Instruments
To appreciate the significance of modern surgical instruments, we must first explore their historical context. Surgical instruments date back thousands of years, with rudimentary tools used for basic surgical procedures in ancient civilizations. The evolution from these ancient tools to today’s sophisticated devices illustrates the remarkable journey of medical science.
- Ancient Egypt: The use of bronze and stone tools.
- Greek and Roman Advances: Innovators like Hippocrates and Galen laid foundational principles.
- The Middle Ages: Limited surgical advancements but saw the birth of specialized guilds.
- Renaissance Period: Rebirth of anatomical studies, leading to improved surgical understanding.
Definition and Characteristics of Modern Surgical Instruments
Modern surgical instruments are specifically designed tools utilized during surgical procedures to cut, grasp, hold, or dissect tissues. They feature advanced materials and precision engineering, ensuring greater effectiveness and safety for patients. Some defining characteristics include:
- Materials: Stainless steel, titanium, and carbon fiber for durability and sterilization.
- Precision: Instruments are crafted to achieve highly specific functions with minimal invasiveness.
- Ergonomics: Designed for optimal handling, reducing surgeon fatigue and improving surgical outcomes.
- Technology Integration: Many instruments now include electronic components for advanced functionalities.
Categories of Modern Surgical Instruments
The broad spectrum of modern surgical instruments can be classified into several categories based on their function and application:
1. Cutting Instruments
These tools are essential for cutting through tissues. Some examples include:
- Scalpels: Precision cutting tools for incisions.
- Scissors: Surgical scissors designed for cutting tissues and sutures.
2. Grasping Instruments
Grasping tools help the surgeon securely hold tissue during procedures. Notable instruments include:
- Forceps: Used to grasp or hold tissues.
- Clamp: Used to ligate blood vessels.
3. Retracting Instruments
Retractors are crucial for holding back tissues and organs during surgery, providing the surgeon with visibility and access:
- Hand-held Retractors: Used manually to open and hold incisions.
- Self-retaining Retractors: Maintain their position without manual holding.
4. Suturing Instruments
These instruments are essential for stitching up wounds post-surgery. Some important types include:
- Suture Needles: Custom-designed needles for specific types of suturing.
- Hemostatic Forceps: Used to control bleeding during and after surgery.
5. Specialized Instruments
Many surgeries require specialized instruments tailored for specific surgical procedures:
- Endoscopic Instruments: Used in minimally invasive surgeries.
- Orthopedic Instruments: Designed for bone surgeries.
- Neurosurgical Instruments: Crafted for surgeries involving the nervous system.
Benefits of Modern Surgical Instruments
The introduction and continuous innovation of modern surgical instruments have brought numerous benefits, significantly affecting surgical practices and patient care:
Enhanced Precision
Surgeons can perform complex procedures with improved accuracy, reducing the risk of complications and ensuring better outcomes.
Reduced Recovery Time
With minimally invasive surgical tools, patients experience less trauma, which leads to quicker recovery and shorter hospital stays.
Lower Infection Rates
Advancements in sterilization methods and materials have contributed to decreased infection rates, enhancing overall patient safety.
Improved Ergonomics
Designed with surgeon comfort in mind, modern surgical instruments reduce fatigue, allowing for longer and more complex procedures.
The Impact of Technology on Surgical Instruments
Technological advancements have dramatically transformed modern surgical instruments:
Robotic Surgery
Robotics has revolutionized the field, allowing surgeons to perform operations with precision and control beyond human capacity.
Improved Visualization
Instruments are now equipped with cameras and imaging tools that provide real-time video feedback, enhancing precision during surgery.
Smart Instruments
Integration of sensors and data analytics into instruments aids in monitoring the surgical process and improving decision-making.
The Future of Modern Surgical Instruments
The landscape of surgical instruments continues to evolve. The future holds exciting potential driven by innovation, including:
Biodegradable Materials
Advancements in materials science may lead to the creation of environmental-friendly, biodegradable surgical instruments that reduce waste.
Personalized Surgical Instruments
With 3D printing technology, customized instruments tailored to the specific anatomy of patients may become the norm, improving outcomes.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
AI may play a role in instrument design, production, and usage, providing assistance during surgery for enhanced precision and safety.
Conclusion
The advancements in modern surgical instruments represent a significant leap in medical technology and patient care. By evolving from basic tools to sophisticated, high-tech instruments, they continue to save lives and improve outcomes. As we look toward the future, the commitment to innovation in the field of surgical instruments will undoubtedly lead to even greater advances in healthcare and medical practices.
For more information on the latest developments in modern surgical instruments, visit new-medinstruments.com.